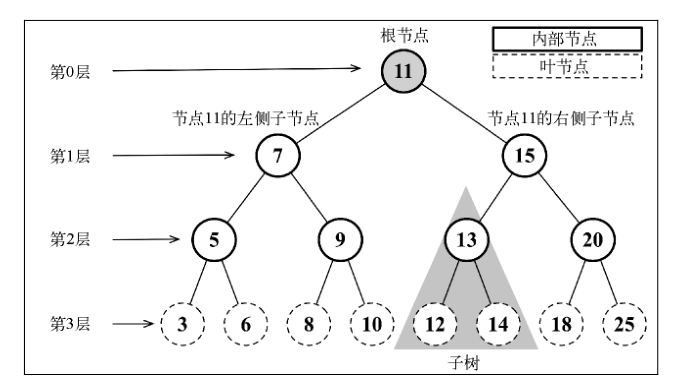
# 定义
- 一种分层数据的抽象模型。
- 前端工作中常见的树包括:DOM 树,级联选择、树形控件等等。
- 一个数结构包含一系列存在父子关系的节点,每个节点都有一个父节点(除了顶部的第一个节点)以及零个或多个子节点。
# 深度/广度优先遍历
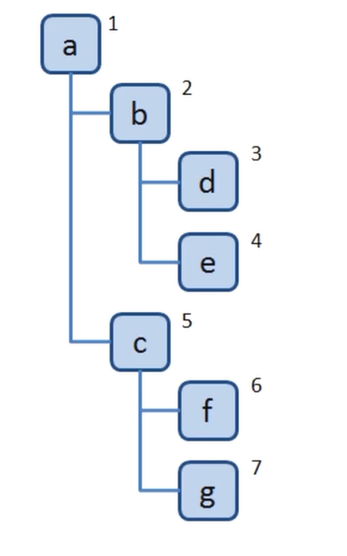
# 深度优先遍历 (DFS)
深度优先遍历:尽可能深的搜索树的分支。类似于我们读书,首先看到章节目录,然后逐个看目录里面的内容。直到看完为止。
深度优先遍历算法有以下要点:
- 访问根节点。
- 对根节点的 children 挨个进行深度优先遍历。
代码实现:
const tree = {
val: 'a',
children: [
{
val: 'b',
children: [
{
val: 'd',
children: [],
},
{
val: 'e',
children: [],
}
],
},
{
val: 'c',
children: [
{
val: 'f',
children: [],
},
{
val: 'g',
children: [],
}
],
}
],
}
const dfs = (root) => {
console.log(root.val)
root.children.forEach(dfs)
}
dfs(tree)
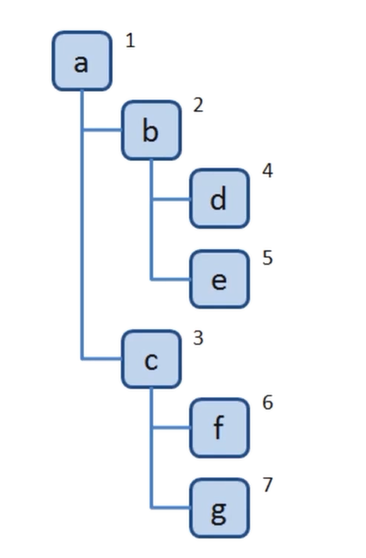
# 广度优先遍历 (BFS)
广度优先遍历:先访问离根节点最近的节点。类似我们刚开始看书的总体目录,看完之后,然后每个章节进行深入去看。
广度优先遍历算法有以下要点:
- 新建一个队列,把根节点入队。
- 把队头出队并访问。
- 把队头的 children 挨个入队。
- 重复第二、三步,直到队列为空。
代码实现:
const bfs = (root) => {
const q = [root]
while(q.length > 0) {
const n = q.shift()
console.log(n.val)
n.children.forEach(child => {
q.push(child)
})
}
}
bfs(tree)
# 二叉树的先中后序遍历
- 树中每个节点最多只能有两个子节点。
- 在 JS 中通常用 Object 来模拟二叉树。
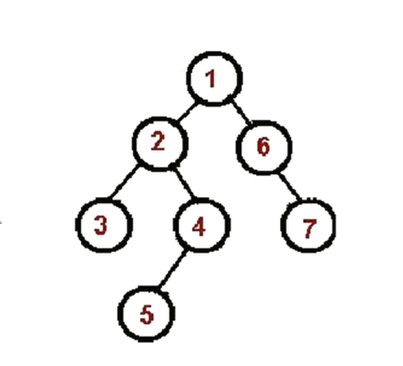
# 先序遍历算法
- 访问
根节点。 - 对根节点的
左子树进行先序遍历。 - 对根节点的
右子树进行先序遍历。
实现代码:
// bt
const bt = {
val: 1,
left: {
val: 2,
left: {
val: 4,
left: null,
right: null
},
right: {
val: 5,
left: null,
right: null
}
},
right: {
val: 3,
left: {
val: 6,
left: null,
right: null
},
right: {
val: 7,
left: null,
right: null
}
}
}
module.exports = bt
const bt = require('./bt')
const preorder = (root) => {
if (!root) return
console.log(root.val)
preorder(root.left)
preorder(root.right)
}
preorder(bt)
# 中序遍历算法
- 对根节点的左子树进行中序遍历。
- 访问根节点。
- 对根节点的右子树进行中序遍历。
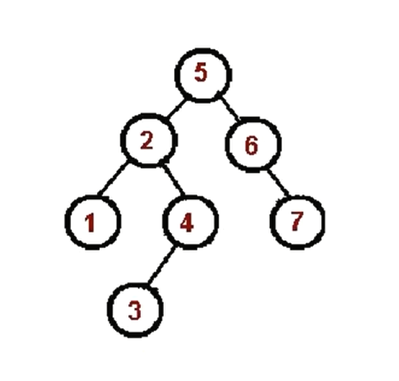
实现代码:
const bt = require('./bt')
const inorder = (root) => {
if (!root) return
inorder(root.left)
console.log(root.val)
inorder(root.right)
}
inorder(bt)
# 后序遍历算法
- 对根节点的左子树进行后序遍历。
- 对根节点的右子树进行后序遍历。
- 访问根节点。
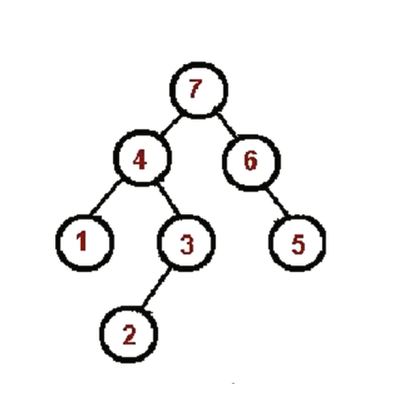
实现代码:
const bt = require('./bt')
const postorder = (root) => {
if (!root) return
postorder(root.left)
postorder(root.right)
console.log(root.val)
}
postorder(bt)
# 二叉树的先中后序遍历 (非递归版)
# 先序遍历
const preorder = (root) => {
if (!root) return
// 函数调用堆栈
const stack = [root]
while(stack.length) {
const n = stack.pop()
console.log(n.val)
if (n.right) stack.push(n.right)
if (n.left) stack.push(n.left)
}
}
# 中序遍历
const inorder = (root) => {
if (!root) return
const stack = []
let p = root
while(stack.length || p) {
while(p) {
stack.push(p)
p = p.left
}
const n = stack.pop()
console.log(n.val)
p = n.right
}
}
# 后序遍历
就是先序遍历的倒序输出;
const postorder = (root) => {
if (!root) return
// 函数调用堆栈
const stack = [root]
const outoutStack = []
while(stack.length) {
const n = stack.pop()
outoutStack.push(n)
if (n.right) stack.push(n.right)
if (n.left) stack.push(n.left)
}
while(outoutStack.length) {
const n = outoutStack.pop()
console.log(n.val)
}
}
# 使用场景
# 二叉树的最大深度
给定一个二叉树,找出其最大深度。
二叉树的深度为根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例: 给定二叉树 [3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
返回它的最大深度 3 。
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/maximum-depth-of-binary-tree
- 解题思路:求最大深度,考虑使用深度优先遍历。在深度优先遍历过程中,记录每个节点所在的层级,找出最大的层级即可。
- 解题步骤:新建一个变量,记录最大深度。然后深度优先遍历整棵树,并记录每个节点的层级,同时不断刷新最大深度这个变量;遍历结束返回最大深度变量。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number}
*/
var maxDepth = function(root) {
let res = 0
const dfs = (n, l) => {
if (!n) return
if (!n.left && !n.right) {
res = Math.max(res, l)
}
dfs(n.left, l +1)
dfs(n.right, l + 1)
}
dfs(root, 1)
return res
};
# 二叉树的最小深度(最短路径算法)
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
说明:叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/minimum-depth-of-binary-tree/
- 解题思路:求最小深度,使用广度优先遍历;在广度优先遍历过程中,遇到叶子节点,停止遍历,返回节点层次。
- 解题步骤:广度优先遍历整棵树,并记录每个节点的层级,遇到叶子节点,返回节点层级,停止遍历。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val, left, right) {
* this.val = (val===undefined ? 0 : val)
* this.left = (left===undefined ? null : left)
* this.right = (right===undefined ? null : right)
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number}
*/
var minDepth = function(root) {
if (!root) return 0;
const stack = [[root, 1]];
while(stack.length) {
const [n, l] = stack.shift();
if (!n.left && !n.right) {
return l;
};
if (n.left) stack.push([n.left, l+1]);
if (n.right) stack.push([n.right, l+1]);
};
};
# 二叉树的层序遍历
给你一个二叉树,请你返回其按层序遍历得到的节点值。(即逐层地,从左到右访问所有节点)。
示例: 二叉树:[3,9,20,null,null,15,7],
3
/ \
9 20
/ \
15 7
返回其层次遍历结果:
[
[3],
[9,20],
[15,7]
]
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-level-order-traversal
- 解题思路:层序遍历顺序就是广度优先遍历,不过在遍历时候需要记录当前节点所处的层级,方便将其添加到不同的数组中。
- 解题步骤:广度优先遍历二叉树,遍历过程中,记录每个节点的层级,并将其添加到不同的数组中。
第一种:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[][]}
*/
var levelOrder = function(root) {
if (!root) return [];
const q = [[root, 0]];
const res = [];
while(q.length) {
const [n, level] = q.shift();
if (!res[level]) {
res.push([n.val]);
} else {
res[level].push(n.val);
}
if (n.left) q.push([n.left, level + 1]);
if (n.right) q.push([n.right, level + 1]);
}
return res;
};
第二种:
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* function TreeNode(val) {
* this.val = val;
* this.left = this.right = null;
* }
*/
/**
* @param {TreeNode} root
* @return {number[][]}
*/
var levelOrder = function(root) {
if (!root) return [];
const q = [root];
const res = [];
while(q.length) {
let len = q.length;
res.push([])
// 循环当前节点的所有子节点
while(len--) {
const n = q.shift();
res[res.length - 1].push(n.val);
if (n.left) q.push(n.left);
if (n.right) q.push(n.right);
}
}
return res;
};
# 二叉树的中序遍历
给定一个二叉树的根节点 root ,返回它的中序遍历。
https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/binary-tree-inorder-traversal/submissions
递归版:
var inorderTraversal = function(root) {
if (!root) return []
const res = [];
const rec = (n) => {
if (!n) return;
rec(n.left);
res.push(n.val);
rec(n.right);
}
rec(root);
return res;
};
非递归版(栈实现):
var inorderTraversal = function(root) {
if (!root) return [];
const res = [];
const stack = [];
let p = root;
while(stack.length || p) {
while(p) {
stack.push(p);
p = p.left;
}
const n = stack.pop();
res.push(n.val);
p = n.right;
}
return res
};
# 路径总和
给定一个二叉树和一个目标和,判断该树中是否存在根节点到叶子节点的路径,这条路径上所有节点值相加等于目标和。
说明: 叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例: 给定如下二叉树,以及目标和 sum = 22,
5
/ \
4 8
/ / \
11 13 4
/ \ \
7 2 1
返回 true, 因为存在目标和为 22 的根节点到叶子节点的路径 5->4->11->2。
链接:https://leetcode-cn.com/problems/path-sum
- 解题思路:在深度优先遍历的过程中,记录当前路径的节点的和。
- 解题步骤:深度优先遍历二叉树,在叶子节点处,判断当前路径的节点值的和是否等于目标值,是就返回 true。遍历结束,如果没有匹配,就返回 false。
var hasPathSum = function(root, sum) {
if(!root) return false;
let res = false;
const dfs = (n, s) => {
// 如果为叶子节点进行判断
if (!n.left && !n.right && s === sum) {
res = true;
}
if (n.left) dfs(n.left, s + n.left.val);
if (n.right) dfs(n.right, s + n.right.val);
}
dfs(root, root.val);
return res;
};
# 遍历 json 的所有节点值
遍历 json 的每个节点的值:
const json = {
a: {
b: {
c: '1'
}
},
d: [1, 2],
}
const dfs = (n, path) => {
console.log(n)
if (n instanceof Object) {
Object.keys(n).forEach(k => {
dfs(n[k], path.concat(k))
})
}
}
dfs(json, [])
antd 中 tree 的渲染:
const json = [
{
title: '一',
key: '1',
children: [{title: '三', key: "3", children: [
{
title: '五',
key: '5',
children: []
}
]}]
},
{
title: '二',
key: '2',
children: [{title: '四', key: "4", children: []}]
}
]
const Demo = () => {
const dfs = (n) =>{
return (
<TreeNode title={n.title} key={n.key}>
{
n.children.map(dfs)
}
</TreeNode>
)
}
return (
<Tree>
{
json.map(dfs)
}
</Tree>
)
}